The Non-Fungible Token (NFT) market has seen a huge leap in popularity in previous year (2021). Sales of nonfungible tokens have increased from $82 million in 2020 to $17.6 billion in 2021 reflecting a huge spike of interest in the new technology. Over 2.4 million new crypto wallet started trading NFTs in 2021, as compared to only 89,000 in 2020. This sudden increase in popularity has attracted huge attention from industrial and scientific communities. It wa widely debated whether NFT ecosystems are the next step in the internet evolution, or they will never find their place in the real world. The non-fungible token technology is in its early stage, and currently it is mostly used in collectibles, arts, and gaming industry.

Technological foundations of NFT
On the picture below you can find a taxonomy of possible NFT applications, dividing it into physical and digital assets.
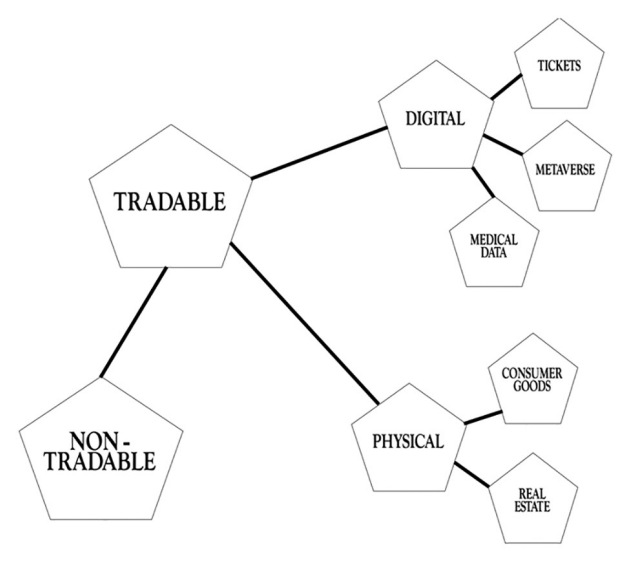
Ticketing – Digitalization of tickets has pushed the entire industry forward, leaving behind many of the problems which were tied to physical tickets, such as: cost of printing and distributing, possibilities of losing or damaging the ticket before the event and many others. New, digital tickets in form of QR codes got rid of these problems, both for the event goers and organizers, still, a lot more can be done to improve the business.
Metaverse – Metaverse is the idea of a perpetual and persistent multiuser virtual environment unifying physical and digital reality.
Real Estate – NFT technology has a huge potential in tokenizing real world assets. Theoretically, owners could issue a token that represents their property, and this token could be sold to interested buyers, completing the process of transferring the ownership with ease. All the information about the property, including when it was built, who was the first owner, how many times it was sold and for what price would be stored on the blockchain without the possibility of tampering.
Medicine – Say you’ve decided to order a direct-to-consumer DNA testing kit in order to have a nutrition plan tailored to your genetic makeup by a private company. You also know that the latter might sell your genetic data to third parties for research purposes. But you settle for the service anyway because it’s the most accurate way to get a personalised diet at a relatively affordable price. However, by selling your genetic data and that of others, the company could be making millions that they will never share with you. Moreover, as such sensitive data get passed along the transaction chain, the risk for mishandling of the information increases. Now, if your genetic data were minted as NFTs, the information will come with an inherent feature to be tracked. You would be able to see where it ends up, and hold those who used it without your permission accountable since you are the sole owner of the data, as certified by the NFT authentication. Moreover, the NFT owner can enable a feature to earn money whenever a transaction occurs with the data.
NFT is a young, emerging technology which could change the future and reshape the market of digital and physical assets. In years ahead of us, there are many chal-
lenges standing in the way of mass adoption. Time will show whether this technology will mature enough and revolutionize above mentioned industries as well, or it will burst like a bubble many are expecting it to be.
©2022. Blockchain laboratory. All Rights Reserved.